Procedures
Endoscopies
Upper digestive tract:
- Diagnostic panendoscopy.
- Esophageal dilation due to benign and malignant strictures (total or partial reduction in esophageal diameter).
- Ligadura de várices esofágicas.
- Endoscopic biopsy for esophageal tumors and inflammatory lesions.
- Taking a gastric biopsy for malignant ulcers and inflammatory lesions.
- Performing percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (without surgery).
- Placement of esophageal prosthesis.
- Coloración de prótesis para vía biliar.
- Colangiopancreatografía retrógrada endoscópica con extracción de litos (piedras) de la vía biliar y/o biopsia por cepillado.
See video: Endoscopía Manga Gástrica
See video: Endoscopía Banda Gástrica
See video: Endoscopía Cancer Gástrico
See video: Colocación de Balón intragástrico
See video: Retiro de Balón intragástrico
See video: Endoscopía Cancer esófago proximal
Lower digestive tract:
- Diagnostic colonoscopy.
- Taking a biopsy of inflammatory lesions.
- Resection of polyps or benign tumors for study (loop polypectomy).
- Hemorrhoidectomy.
See video: Colonoscopía
See video: Enfermedad diverticular del colon
See video: Rectoscopía: Fístula de Hartman en ileorecto anastómosis termino lateral
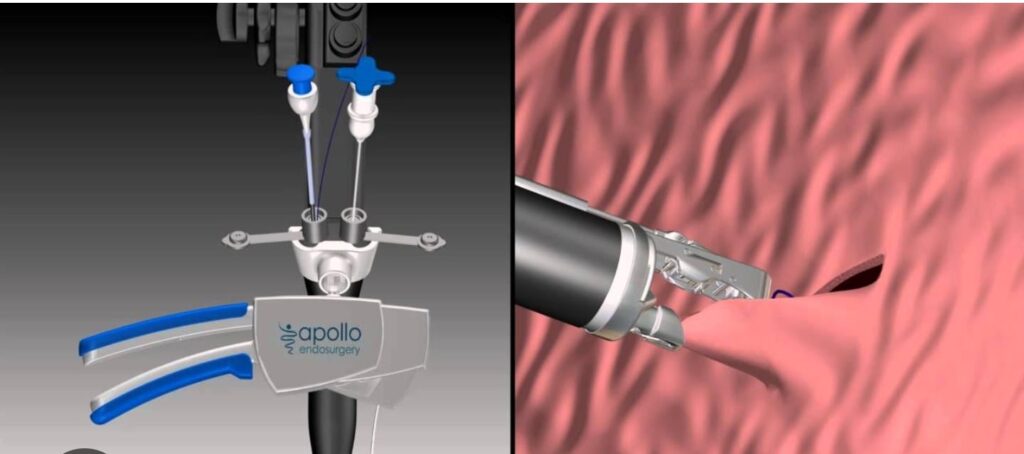
Endoscopy by Apollo Method
Apollo Method
The Apollo Method, also known as Endoscopic Vertical Gastroplasty or Endosleeve, is an innovative technique for stomach reduction without the need for surgery. This procedure is performed via endoscopy, meaning the stomach is accessed through the mouth, without external incisions.
How It Works
During the procedure, between 4 and 6 sutures are applied to the greater curvature of the stomach, reducing its size and creating a tubular shape. This limits the stomach’s capacity to hold food, helping to induce a feeling of fullness with less food.
Benefits
- Minimally Invasive: Does not require incisions or open surgery.
- Quick Recovery: Being an outpatient procedure, recovery is faster compared to traditional surgeries.
- Reversible: Unlike other bariatric techniques, the Apollo Method is reversible.
Results
Patients can expect significant weight loss, generally between 15% and 20% of total body weight in the first year.
Additionally, improvements are observed in obesity-related conditions such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Diagnostic Endoscopy
Diagnostic Endoscopy
Diagnostic endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to directly observe the inside of the body to diagnose various conditions. This procedure is performed using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light at the end, which is inserted into the body through a natural opening, such as the mouth or rectum. Diagnostic endoscopy is commonly used to examine the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
How It Is Performed
Diagnostic endoscopy is performed by inserting an endoscope, which is a flexible tube with a camera and light at the end, through a natural opening in the body, such as the mouth or rectum. The patient usually lies on their side and is given local anesthesia in the throat to reduce sensitivity and facilitate the passage of the endoscope. In some cases, sedatives are also used to help the patient relax and sleep during the procedure. During the examination, the doctor carefully guides the endoscope through the digestive tract. The endoscope transmits real-time images to a screen, allowing the doctor to directly observe the inside of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. If necessary, the doctor can take biopsies or perform other diagnostic procedures during the endoscopy.
How It Works
The endoscope is equipped with a high-resolution camera and a light source that illuminates the inside of the digestive tract. The images captured by the camera are transmitted to a monitor, where the doctor can observe and evaluate any abnormalities. Additionally, the endoscope may have working channels through which instruments can be introduced to take biopsies, remove polyps, or perform other procedures.
Results
The results of the diagnostic endoscopy may be available immediately if the doctor observes any abnormalities during the procedure. If biopsies are taken, the samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results may take several days or weeks to be available. The final report will include details of any findings, such as the presence of ulcers, polyps, inflammations, or tumors, as well as the results of biopsies and other studies performed.
Therapeutic Endoscopy
Therapeutic Endoscopy
Therapeutic endoscopy, on the other hand, is not only used for diagnosis but also to treat various medical conditions. This procedure allows doctors to perform minimally invasive interventions using the endoscope. For example, it can be used to stop internal bleeding, remove polyps, dilate strictures (narrowings), and extract foreign bodies.
How It Is Performed
Therapeutic endoscopy is performed similarly to diagnostic endoscopy but with the additional goal of treating certain conditions. The endoscope is inserted through the mouth or rectum, and the patient is usually sedated for greater comfort. During the procedure, the doctor can use a variety of specialized instruments that are introduced through the working channel of the endoscope to perform therapeutic interventions.
How It Works
The therapeutic endoscope works similarly to the diagnostic endoscope but is equipped with additional tools to perform treatments. These tools may include biopsy forceps, loops for polyp resection, needles for medication injection, probes for blood vessel coagulation, and stents to keep narrowed pathways open.
Results
The results of therapeutic endoscopy can be immediate, especially if the procedure is performed to treat an acute condition, such as stopping bleeding or removing a polyp. In other cases, the results may include the improvement of the patient’s symptoms and the resolution of the treated condition. The doctor will provide a detailed report on the procedure performed, the findings, and any additional treatment that may be necessary.
Bariatric Endoscopy
Definition
Bariatric endoscopy is a set of minimally invasive procedures performed via endoscopy to treat overweight and obesity. These procedures are used as a less invasive alternative to traditional bariatric surgery and are designed to reduce the volume of the stomach, helping patients feel full with less food and thus lose weight.
How It Is Performed
Bariatric endoscopy is carried out using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light at the end, which is inserted through the patient’s mouth. Depending on the type of procedure, different techniques can be used:
- Gastric Balloon: A silicone balloon is inserted into the stomach and filled with saline solution to occupy space and reduce the stomach’s capacity. This balloon is left in place for several months.
- APOLLO Method: The stomach wall is sutured to reduce its size and capacity. This is done via endoscopy and does not require external incisions.
- POSE Method: Folds are created in the stomach to reduce its capacity. This procedure is also performed via endoscopy and does not require incisions.
Before the procedure, the patient must fast for at least 8 hours and not consume water for 4 hours prior. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort.
How It Works
The endoscope used in bariatric endoscopy is equipped with a high-resolution camera and a light source that allows the doctor to visualize the inside of the stomach in real-time. Through the working channel of the endoscope, various instruments can be introduced to perform the necessary procedures, such as placing the gastric balloon or suturing the stomach wall. The main goal of these procedures is to reduce the volume of the stomach, helping patients feel full with less food and thus reduce their caloric intake and lose weight. Additionally, these procedures are minimally invasive, meaning they have a lower risk of complications and a shorter recovery time compared to traditional bariatric surgery.
Results
The results of bariatric endoscopy can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient. In general, patients can expect significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
The long-term success of bariatric endoscopy largely depends on the patient’s commitment to lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise. Patients are usually discharged 24 hours after the procedure and can return to their normal activities within a few days.
In summary, bariatric endoscopy is an effective and less invasive option for the treatment of overweight and obesity, offering promising results in terms of weight loss and overall health improvement.

Endoscopic gastroplasty
It is a minimally invasive procedure that reduces the size of the stomach through internal sutures, without the need for open surgery. It is performed using an endoscope, a thin tube with a camera at the end, inserted through the mouth. Indications:
- Obesity: Ideal for people with a high body mass index (BMI) who have not been successful with diets and exercise.
- Obesity-related diseases: Type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, etc.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive: Faster recovery and fewer complications.
- No incision required: Less pain and scarring.
- Long-lasting results: Alters the anatomy of the stomach.
- Outpatient procedure: In many cases, does not require prolonged hospitalization.
Disadvantages and comparison with other techniques:
- Not for everyone: Not suitable for people with certain medical conditions or severe morbid obesity.
- Individual results: Weight loss can vary between patients.
- Cost: May be more expensive than other treatments. Comparison with other bariatric techniques: Minimally difficult to reverse.
Endoscopic gastroplasty is an excellent option for many people with obesity, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery. However, it is important to evaluate each case individually and consider the pros and cons with a specialist. If you have an aversion to surgery, any obesity problem, overweight, or metabolic disease, schedule your appointment, we will gladly advise you.
Information for you
Intragastric balloon
Travel plans
Learn how to schedule and plan your surgery
We offer you excellent stay and travel plans so that you don’t have to worry about anything at the time of your surgeries or treatments.

